|
I am a Postdoctoral Researcher at Aalto University working on LLMs, reinforcement learning (RL), and structures for systematic thinking in language models. I am working with Samuel Kaski and Pekka Marttinen, and I coordinate the Foundation models for language & reinforcement learning team at FCAI, the Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence. Previously, I obtained my PhD from Google Research (through the CIFRE scheme), Inria and Ecole Normale Superieure in Paris. My PhD research focused on RL and learning from demonstration for robotic manipulation. In particular, I still actively work on learning reward models, multi-modality and embodied AI, topics I explored during my PhD. I defended my thesis on Autonomous and Weakly-Supervised Learning for Robotic Manipulation in December 2022 and I was advised by Cordelia Schmid, Jean Ponce and Julien Mairal. At Inria, I was a member of the Willow and Thoth teams.
Email |
CV |
Google Scholar |
|

|
|
There are considerable mutual benefits to be gained from integrating ideas from reinforcement learning (RL) and language models. LLMs possess a real-world knowledge base that is vast but mostly static, and not specific enough for many environments. Moreover, decoding is typically greedy, without planning or lookahead. RL, on the other hand, formalizes learning from interaction, trading off exploration and short-term reward maximization, and planning with the future in mind. My objective is twofold: I aim to equip RL agents with world knowledge and transferable skills that models like LLMs and VLMs have learned from internet-scale text and vision corpora. Furthermore, I am looking to teach LLMs to think and plan more explicitly – using utilities such as tree search, task decomposition and code – and to learn from embodied interaction like RL agents. |
|
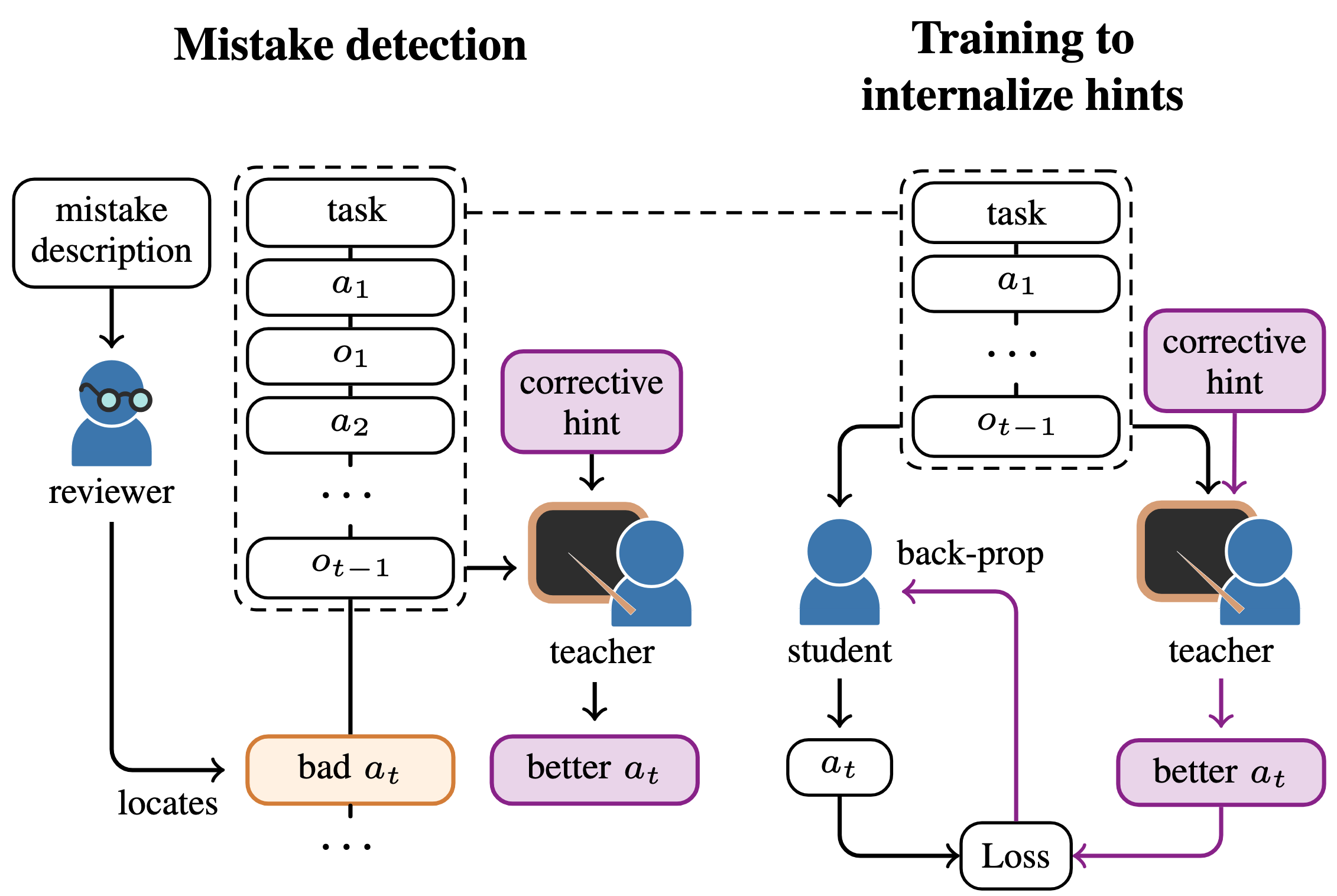
Minttu Alakuijala*, Ya Gao*, Georgy Ananov*, Samuel Kaski, Pekka Marttinen, Alexander Ilin, Harri Valpola In review, 2025 arXiv We train LLM agents to internalize knowledge and skills for multiple tasks without relying on ever-expanding prompts or prior demonstrations, through context distillation and efficient use of corrective feedback from humans. |
|
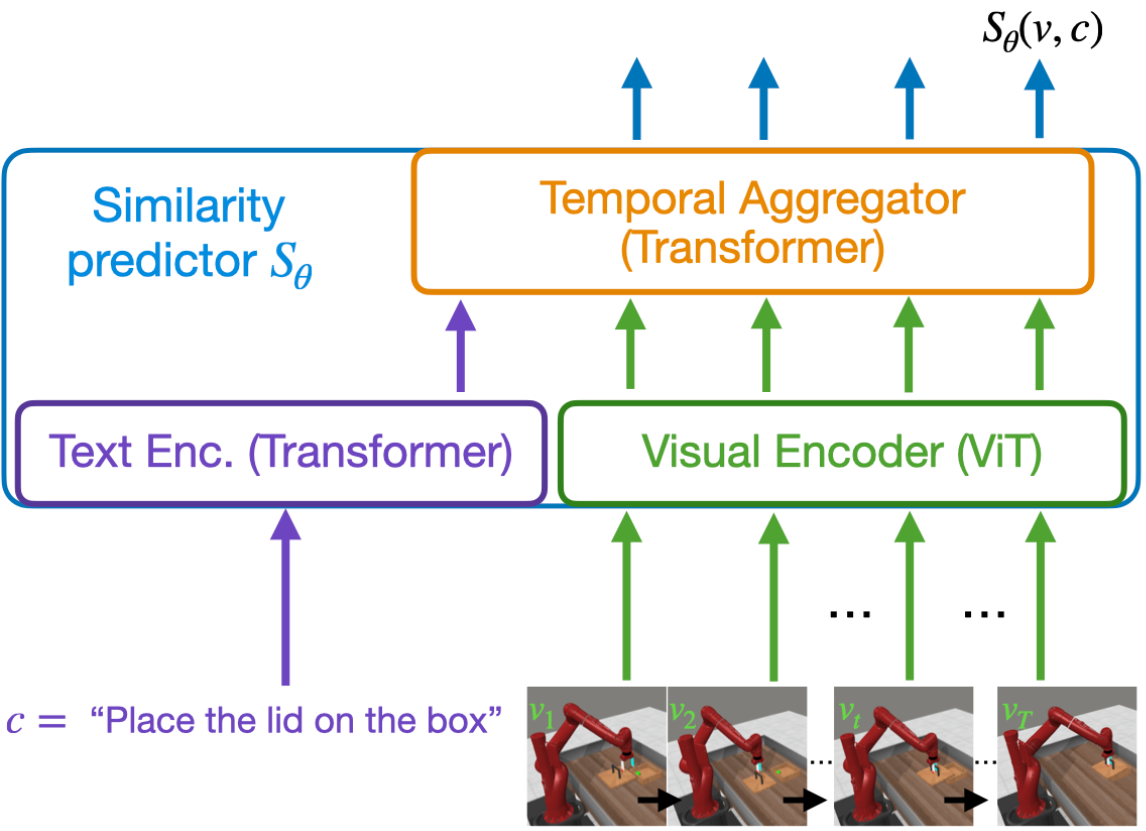
Minttu Alakuijala, Reginald McLean, Isaac Woungang, Nariman Farsad, Samuel Kaski, Pekka Marttinen, Kai Yuan TMLR, 2025 arXiv We train language-conditioned robotic reward functions from actor-agnostic data, and outperform 5 existing methods with a novel combination of contrastive and sequential ranking objectives, together ensuring both smooth and accurate rewards. |
|
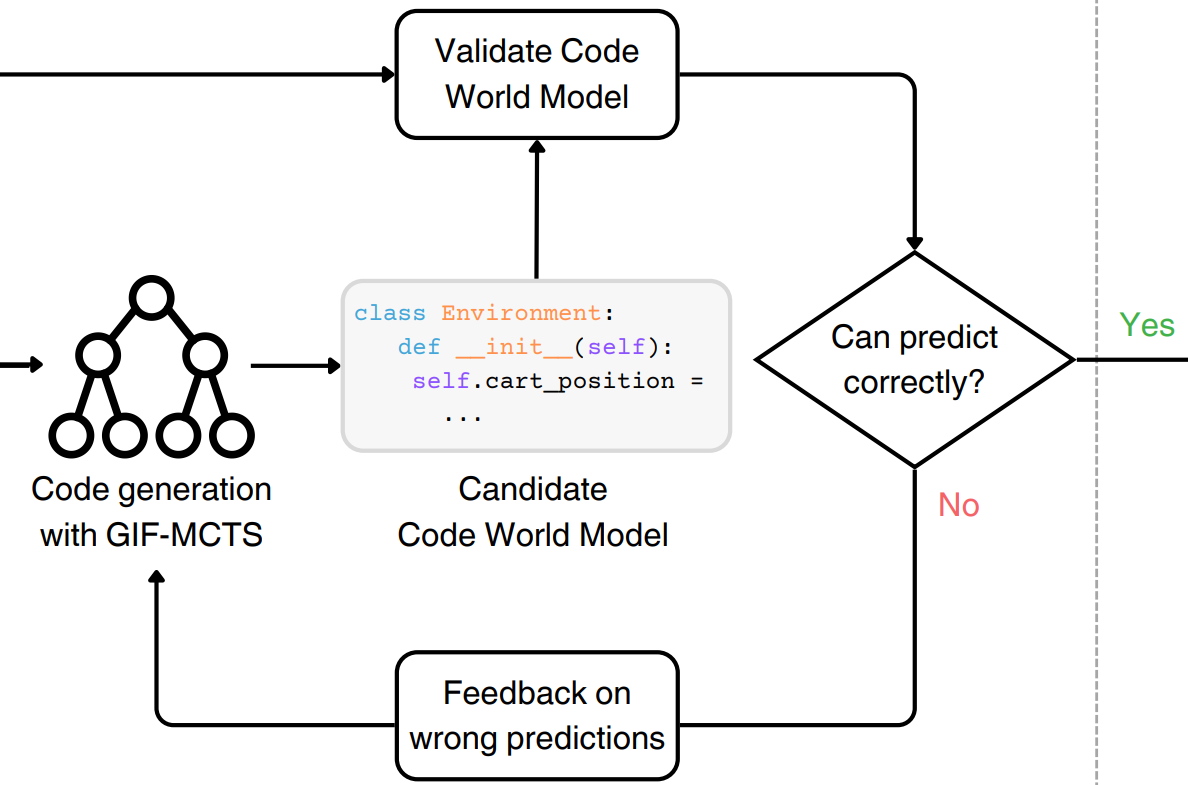
Nicola Dainese, Matteo Merler, Minttu Alakuijala, Pekka Marttinen NeurIPS 2024 arXiv We propose to model RL environments with code written by an LLM, propose a method to improve code generation for this task and show how to plan with code world models. |
|
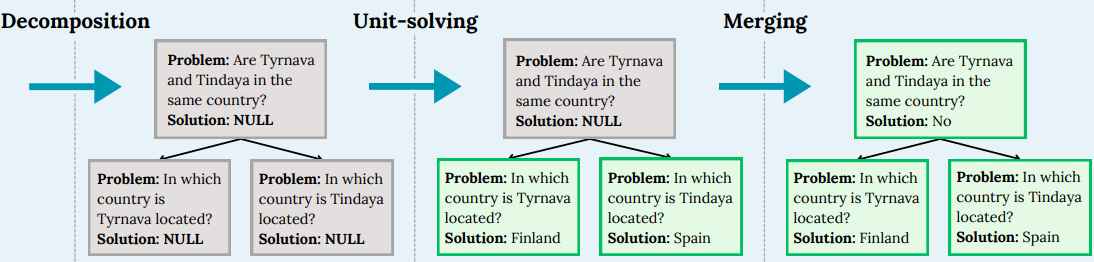
Sergio Hernandez-Gutierrez, Minttu Alakuijala, Alexander Nikitin, Pekka Marttinen NeurIPS 2024 Workshop on System 2 Reasoning at Scale Paper We present a novel divide-and-conquer method to solve reasoning problems with LLMs, employing recursive decomposition with dependency modeling in generic settings. |
|
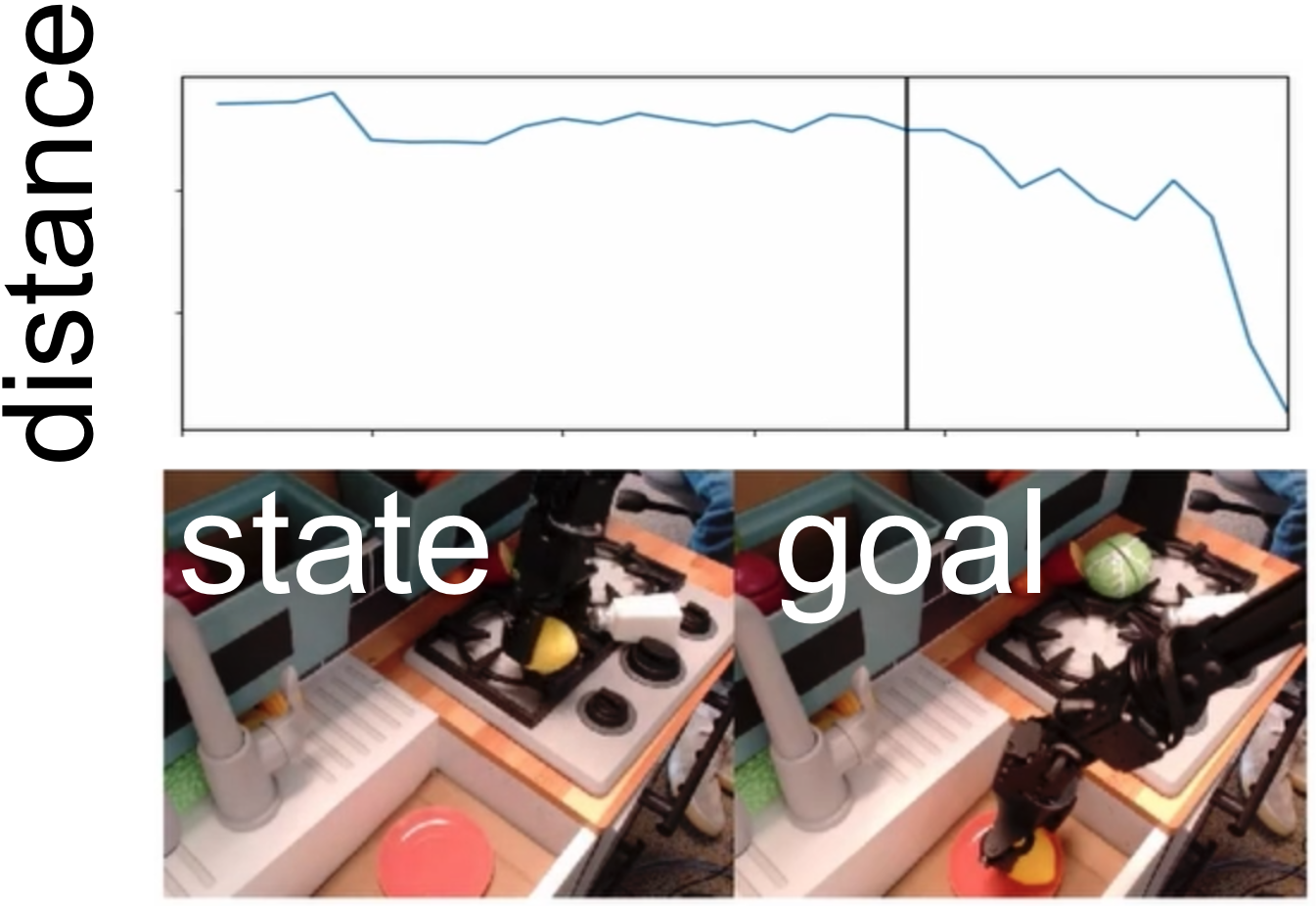
Minttu Alakuijala, Gabriel Dulac-Arnold, Julien Mairal, Jean Ponce, Cordelia Schmid ICRA, 2023 project page | arXiv We learn dense reward functions for robotic manipulation by learning about distances in state space from videos of humans only, using self-supervised contrastive and regression objectives. |
|
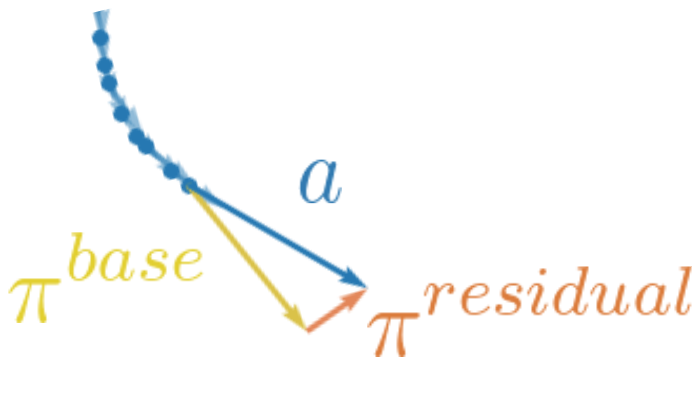
Minttu Alakuijala, Gabriel Dulac-Arnold, Julien Mairal, Jean Ponce, Cordelia Schmid RSS 2020 Workshop on Advances & Challenges in Imitation Learning for Robotics project page | arXiv Starting from a small number of task demonstrations on a robot arm, we learn an initial base policy and a task-relevant, low-dimensional representation space through behavioral cloning, which is then autonomously improved through residual reinforcement learning using images, proprioceptive inputs and sparse rewards only. |

|
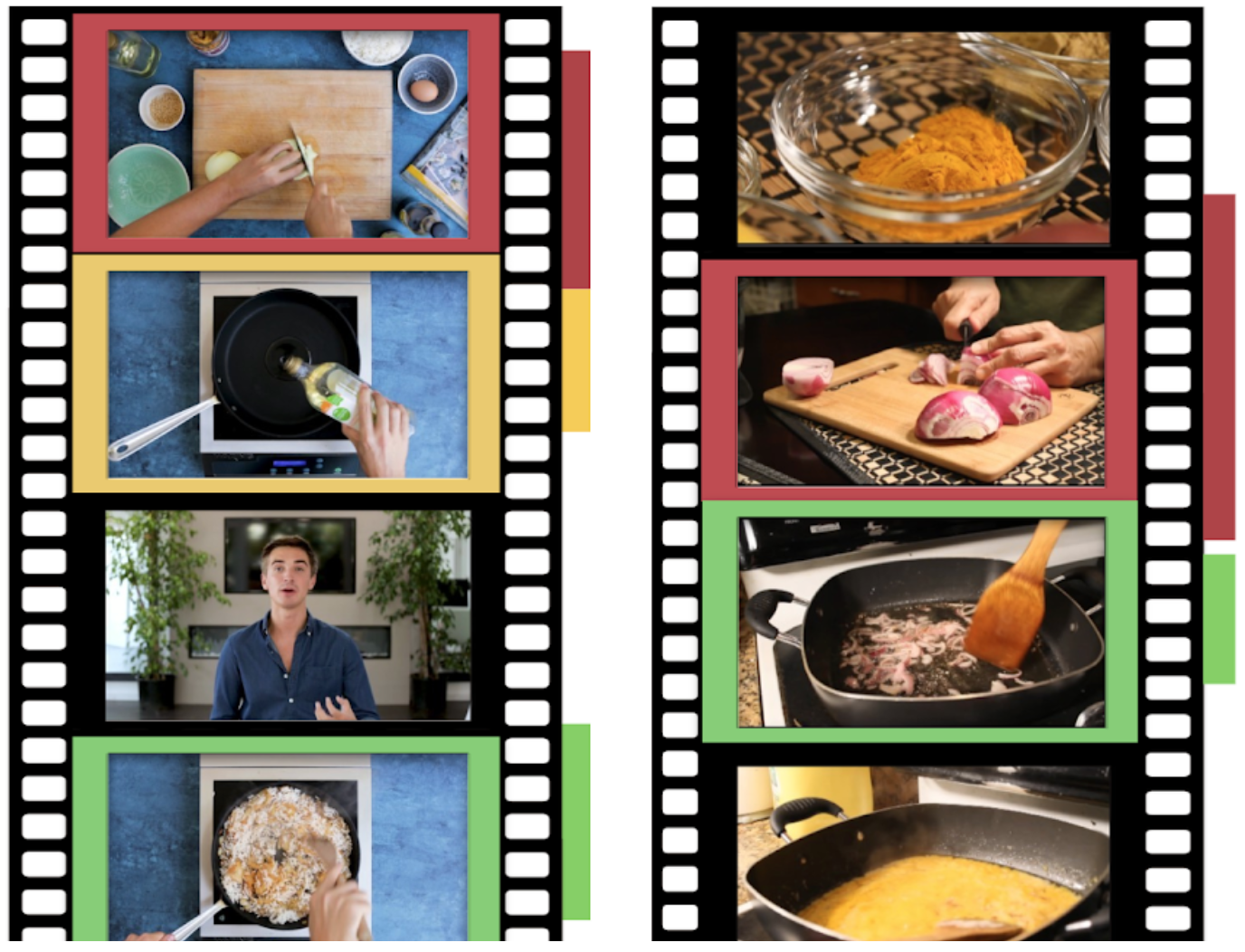
Minttu Alakuijala, Julien Mairal, Jean Ponce, Cordelia Schmid CVPR 2020 Workshop on Learning from Instructional Videos video | poster Using only weak supervision from the timing of narration and visual information, we segment narrated tutorial videos into k action classes or background. We use a discriminative clustering objective together with an inconsistency penalty which encourages the timing and order of actions in the visual stream to match that of the narration stream in each video. |
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron's website. |